Overcoming Problems
Debugging!
Technical things not doing what you expect or need them to do can be a very frustrating experience
What experience do you have with debugging?
Read
Rubberduck
Ask
blank
Check the error message, what does the software say the problem is?
Read
Rubberduck
Ask
blank
Go through the code line by line and explain to a 'rubber duck' what is going on and try and spot the error
Read
Rubberduck
Ask
blank
Talk to an expert in your organisation, or search for the solution on StackOverflow
To improve accuracy, quality and usefulness any errors should be corrected, imputed or rejected
Activity
In groups choose a couple of the scenarios on the next slide and discuss how you would mitigate or solve them
| Data isn't available as planned |
| A team member has not delivered what you need |
| Technical failure resulting in work lost |
| Project is taking longer than forecast |
| Critical team member leaves the company suddenly |
| Key stakeholder changes the scope mid project |
| Client wants delivery deadline brought forward |
| Becomes clear you cannot deliver what was promised to client |
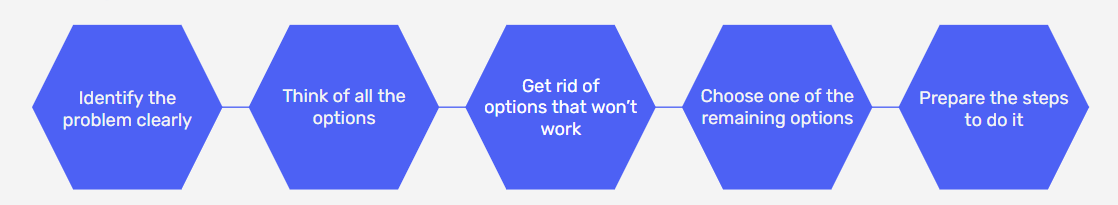
Form an Action Plan
1. Confirm and identify the problem
2. Quantify and describe- what is the impact?
3. What are the potential next steps?
4. Communicate to stakeholders and confirm desired next steps
5. Adjust plan and circulate
6. Continue to new plan, repeat if necessary
Can this problem be solved?
Do one thing at a time
Focus on what you can control
Sometimes doing nothing is best
Quality Control
What issues might we have creating a table with these field names?
| Subscribers |
| subID |
| firstName |
| surname |
| email |
| birthday |
Truncation
Corruption
Missing Data
Data Types
Translation
blank
Precision is lost when the data is stored somewhere too short to hold its entire length
Truncation
Corruption
Missing Data
Data Types
Translation
blank
Commas, apostrophes and other delimeters are moved/lost maing the table unreadable
Truncation
Corruption
Missing Data
Data Types
Translation
blank
Rows go missing when only a portion of the data is uploaded
Truncation
Corruption
Missing Data
Data Types
Translation
blank
Data mismatch from wrong data types being entered into fields
Truncation
Corruption
Missing Data
Data Types
Translation
blank
Encoding is wrong or symbols or rich characters are lost
Common tools to help us be confident in our data accuracy
Count the data
Spot checks
Calculate aggregates
Export comparison
Activity
In groups discuss:
- Why is quality control important?
- Whose responsibility is quality control?
- When should quality control occur?
- How should quality control be recorded?
- What should you if somehting fails quality control?
| 6 Core Data Quality Dimensions |
| Completeness |
No missing values |
| Uniqueness |
Data only stored in one place |
| Timeliness |
Data should be reasonably up to date |
| Validity |
Conforms to the correct syntax |
| Accuracy |
Value stored is correct for its occurrence |
| Consistency |
Form and content of field is always the same |
In summary...
Quality control gives us confidence in results
Simple techniques can be used to check uploads, simple queries can be used to check results
Checking the quality as you go is easier and more efficient than doing it at the end
Code can be designed to be more robust
Performance Techniques
Performance issues can arise due to...
Too much data
Inefficient queries
Over complex queries (too many joins)
Database is not normalised properly
What is the quickest way to find a topic in an encyclopedia?
Indexing
Every record in a database is assigned an index
Data is retrieved by referencing the index
| Index |
Letter |
Phonetic |
| 1 | A | Alpha |
| 2 | B | Bravo |
| 3 | C | Charlie |
| 4 | D | Delta |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 25 | E | Yankee |
| 26 | F | Zulu |
Denormalisation
A database optimisation technique where redundant data is added to one or more tables to help avoid costly joins in a relational database.
Denormalisation
Pros
- Data retrieval is faster through fewer joins
- Queries are simpler through looking at fewer tables
Cons
- Updates and inserts are more expensive and harder to write
- Data may be inconsistent
- Data redundancy requires more storage
| date |
month |
sales |
country |
code |
continent |
| 08/06/2020 |
6 |
791 |
France |
FR |
Europe |
| 08/06/2020 |
6 |
582 |
Canada |
CA |
North America |
| 08/06/2020 |
6 |
915 |
Egypt |
EG |
Africa |
| 08/06/2020 |
6 |
787 |
Norway |
NO |
Europe |
| country |
wins |
draws |
losses |
win % |
| France |
6 |
1 |
0 |
85.7% |
| Croatia |
6 |
0 |
1 |
85.7% |
| Belgium |
6 |
0 |
1 |
85.7% |
| England |
4 |
0 |
3 |
57.1% |
Database Maintenance
Maintaining a database is critical to ensuring a database environment performs reliably and efficiently. We need these tasks to:
→ Increase performance
→ Free up disk space
→ Check for data errors
→ Check for hardware faults
Log File Maintenance
Log files are invaluable for diagnosing problems in your database and should therefore be saved.
They can however be quite large (especially at high debug levels) and so should be discarded after a reasonable period of time.
Read more here.
Fragmentation
Indexes can become fragmented as new data is introduced which can affect performance
| id |
name |
| 1 |
Jane |
| 2 |
Peter |
| 3 |
Kim |
| 4 |
Olivia |
| id |
name |
| 1 |
Jane |
| |
|
| 3 |
Kim |
| 4 |
Olivia |
| 5 |
Suresh |
| id |
name |
| 1 |
Jane |
| |
|
| 3 |
Kim |
| |
|
| 5 |
Suresh |
Other Techniques:
Data Compaction
Integrity Check
Backing Up
Compress the data so it can be stored more efficiently and quickly
Other Techniques:
Data Compaction
Integrity Check
Backing Up
Ensure relationships between entities have been observed
Other Techniques:
Data Compaction
Integrity Check
Backing Up
Regularly back your data up!
